Photon Counting Detectors
PDM Series
Single Photon Avalanche Diodes
- Timing resolution down to < 50 ps (FWHM)
- Detection efficiency up to 49 %
- Different active areas: 20, 50, and 100 µm
- Ultra stable at high count rates
 The photon counting detector modules of the PDM Series are all solid-state instruments designed and manufactured by Micro Photon Devices (MPD). They feature an excellent photon detection efficiency and superior timing resolution, which is obtained through the use of epitaxial silicon Single Photon Avalanche Diodes (SPAD) and patented integrated Active Quenching Circuits (iAQC). The SPADs are specifically designed and optimized for time-resolved photon counting applications.
The photon counting detector modules of the PDM Series are all solid-state instruments designed and manufactured by Micro Photon Devices (MPD). They feature an excellent photon detection efficiency and superior timing resolution, which is obtained through the use of epitaxial silicon Single Photon Avalanche Diodes (SPAD) and patented integrated Active Quenching Circuits (iAQC). The SPADs are specifically designed and optimized for time-resolved photon counting applications.
Timing resolution down to 50 ps
 The SPADs of the PDM Series generate two output signals - a counting output (TTL signal) and a timing output (NIM signal), which provides better than 50 ps (FWHM) photon timing resolution for a wide range of detection wavelengths. Especially above 470 nm the temporal response is even comparable to MCP-PMTs and an Instrument Response Function (IRF) around 50 ps can be reached with fast TCSPC electronics along with a suited short pulsed laser.
The SPADs of the PDM Series generate two output signals - a counting output (TTL signal) and a timing output (NIM signal), which provides better than 50 ps (FWHM) photon timing resolution for a wide range of detection wavelengths. Especially above 470 nm the temporal response is even comparable to MCP-PMTs and an Instrument Response Function (IRF) around 50 ps can be reached with fast TCSPC electronics along with a suited short pulsed laser.
Different active sensor areas
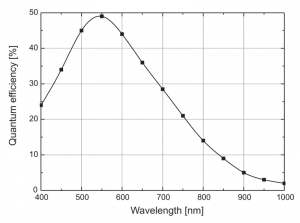
 The SPADs are available with a diameter of the active area of 20, 50 or 100 µm, different dark count grades and can be supplied with an easy to use FC/PC connection for optical fibers or as a free-beam module. The PDM SPADs cover a spectral range from about 400 nm to 1000 nm with the highest quantum efficieny in the VIS range around 550 nm. They are extremely robust and can withstand continuous exposition to daylight. The high quantum efficiency make them an ideal detector for single molecule applications, like Fluorescence Correlation Spectroscopy (FCS) or Fluorescence Lifetime Imaging (FLIM), especially as the SPAD output has a stable timing even at count rates exceeding 1 million counts/sec.
The SPADs are available with a diameter of the active area of 20, 50 or 100 µm, different dark count grades and can be supplied with an easy to use FC/PC connection for optical fibers or as a free-beam module. The PDM SPADs cover a spectral range from about 400 nm to 1000 nm with the highest quantum efficieny in the VIS range around 550 nm. They are extremely robust and can withstand continuous exposition to daylight. The high quantum efficiency make them an ideal detector for single molecule applications, like Fluorescence Correlation Spectroscopy (FCS) or Fluorescence Lifetime Imaging (FLIM), especially as the SPAD output has a stable timing even at count rates exceeding 1 million counts/sec.
| Photon Detection Efficiency (typical, without FC connector) | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| @ 400 nm | 24 % | ||
| @ 550 nm | 49 % | ||
| @ 650 nm | 37 % | ||
| Losses due to fiber connector: < 20 % absolute | |||
| Dark Counts | |||
| SPAD diameter | 20 µm (on request) | 50 µm | 100 µm |
| Available selections | < 25 cps < 5 cps |
< 250 cps < 100 cps < 50 cps < 25 cps |
< 500 cps < 250 cps < 100 cps < 50 cps < 25 cps |
| Single Photon Timing Resolution | |||
| Counting output, TTL signal (FWHM) | 250 ps | ||
| Timing output, NIM signal (FWHM) | down to 50 ps, increases in blue/UV spectral range | ||
| Afterpulsing Probability | |||
| Maximum | 3 % | ||
| Input/Output | |||
| Dead time | 77 ns (typical) | ||
| Output signal | TTL for counting output and NIM for timing output* | ||
| Output pulse rise and fall times | < 2 ns on 10 pF load | ||
| Output pulse duration | 20 ns (typical) | ||
| Gating input | TTL control (low level gates detector off) | ||
| Supply input connector | standard 3.5 mm supply socket | ||
| Operating conditions | |||
| Supply Voltage | unregulated DC, any value 5 V–12 V | ||
Typical detection efficiency vs. wavelength
All Information given here is reliable to our best knowledge. However, no responsibility is assumed for possible inaccuracies or omissions. Specifications and external appearances are subject to change without notice.
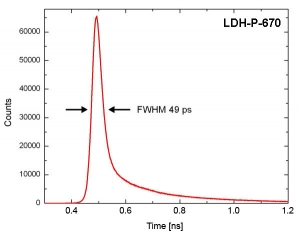
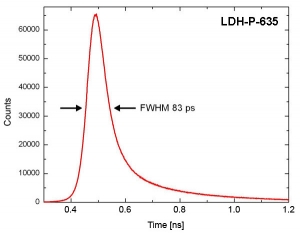
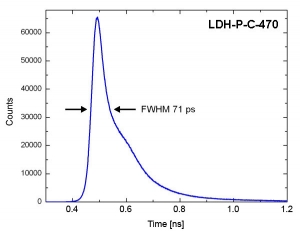
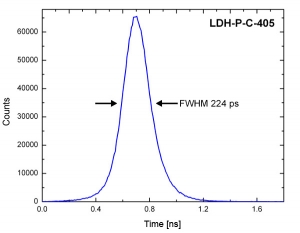
The graphs below show examples of the measured instrument response functions (IRF) of a PDM module with an active area of 50 µm. The measurements were taken with the PicoHarp 300 TCSPC module and different laser heads of the LDH series driven by the PDL 800-D.
The measured full width at half maximum (FWHM) is 48 ps for the excitation at 670 nm. Taking the exceptionally short pulse width of the excitation laser of 32 ps into account, this results in a timing response of the SPAD of 37 ps.
The measured full width at half maximum (FWHM) is 72 ps for the excitation at 470 nm. Taking the pulse width of the excitation laser of 56 ps into account, this results in a timing response of the SPAD of 44 ps.
The single photon sensitive detectors of the PDM Series can be used in various applications, where the high sensitivity and very good timing resolution of the detector are important, such as:
- Time-Resolved Fluorescence
- Fluorescence Lifetime Imaging (FLIM)
- Phosphorescence Lifetime Imaging (PLIM)
- Fluorescence Correlation Spectroscopy (FCS)
- Fluorescence Lifetime Correlation Spectroscopy (FLCS)
- Foerster Resonance Energy Transfer (FRET)
- Stimulated Emission Depletion Microscopy (STED)
- Dual Focus Fluorescence Correlation Spectroscopy (2fFCS)
- Pulsed Interleaved Excitation (PIE)
- Single Molecule Spectroscopy / Detection
- Time-Resolved Photoluminescence (TRPL)
- TRPL Imaging
- Lanthanide Upconversion
- Bunch Purity
- LIDAR/Ranging/SLR
- Antibunching
- Coincidence Correlation
- Quantum Communication
- Quantum Entanglement
- Quantum Teleportation
- Quantum Information Processing
The following documents are available for download:
Latest 10 publications referencing SPADs
The following list is an extract of 10 recent publications from our bibliography that either bear reference or are releated to this product in some way. Do you miss your publication? If yes, we will be happy to include it in our bibliography. Please send an e-mail to info@picoquant.com containing the appropriate citation. Thank you very much in advance for your kind co-operation.




 Contact us
Contact us